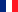
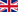
Etchmiadzin Cathedral
The original church was built in the early fourth century — between 301 and 303 according to tradition—by Armenia's patron saint Gregory the Illuminator, following the adoption of Christianity as a state religion by King Tiridates III. It replaced a preexisting temple, symbolizing the conversion from paganism to Christianity. The core of the current building was built in 483/4 by Vahan Mamikonian after the cathedral was severely damaged in a Persian invasion. From its foundation until the second half of the fifth century, Etchmiadzin was the seat of the Catholicos, the supreme head of the Armenian Church.
Although never losing its significance, the cathedral subsequently suffered centuries of virtual neglect. In 1441 it was restored as catholicosate and remains as such to this day. Since then the Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin has been the administrative headquarters of the Armenian Church. Etchmiadzin was plundered by the Safavids in 1604, when relics and stones were taken out of the cathedral to New Julfa in an effort to undermine Armenians' attachment to their land. Since then the cathedral has undergone a number of renovations. Belfries were added in the latter half of the seventeenth century and in 1868 a sacristy was constructed at the cathedral's east end. Today, it incorporates styles of different periods of Armenian architecture. Diminished during the early Soviet period, Etchmiadzin revived again in the second half of the twentieth century, and under independent Armenia.
As the main shrine of religious Christian Armenians worldwide, Etchmiadzin has been an important location in Armenia not only religiously, but also politically and culturally. A major pilgrimage site, it is one of the most visited places in the country. Along with several important early medieval churches located nearby, the cathedral was listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2000.